Contact us

(*Required fields)
Please fill in ALL of the required information to submit this form.
Oral and maxillofacial surgery specializes in treating injuries, defects and pathologies in the face, jaw, hard and soft tissues of the oral and maxillofacial region. We have a special team of oral surgeons and general dentists, to deal with conditions like the impacted tooth, maxillofacial trauma and other situations which involve surgery.
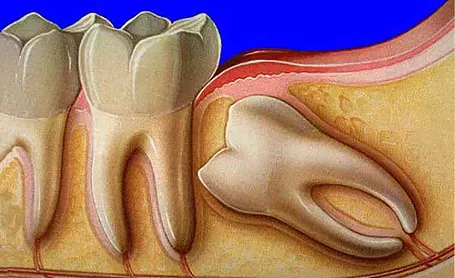
Often the third molar or the wisdom teeth either fail to come through in proper alignment or they fail to emerge at all. This causes the impacted wisdom teeth that are trapped between the gum tissue and jawbone. They may be full bony impacted or partial bony impacted.
A person with impacted tooth may present with the following symptoms-
Evaluation – After enquiring about the signs and symptoms from the patient, the next step would be an oral examination and panoramic radiography or OPG. Based on the findings, our oral surgeons then plan the approach for wisdom tooth extraction.
Procedure – The extraction is done under local anaesthesia and sterile environment. Minor surgery is performed where the tissue and bone around the impacted tooth are removed so that the tooth can be cleanly extracted from the socket. Stitches are given to promote healing of the overlying tissue, for 5 to 7 days.

A Frenectomy is the removal of frenulum, a small fold of tissue attaching the lip and cheek to the alveolar mucosa and gingiva. When the procedure is performed inside the middle of upper lip, it is called as Labial Frenectomy and when under the tongue, it is known as Lingual Frenectomy. This surgery may be performed for the following reasons-
Procedure – We at TnSS use advanced technology of electrosurgery and Laser, for frenectomy, with the advantage of shorter duration of surgery, the simplicity of the procedure, the absence of postoperative infections, lessen pain and swelling, and a small or no scar.
Our team of oral surgeons are well versed in emergency care, acute treatment and long-term reconstruction. They are well trained, skilled and experienced to treat patients with physical trauma as well as handle the emotional trauma associated with it. Our high standards of sterilization protocol ensure sterile atmosphere during treatment while our high-end technology ensures quick healing and alleviation of pain. We take care of the following conditions-
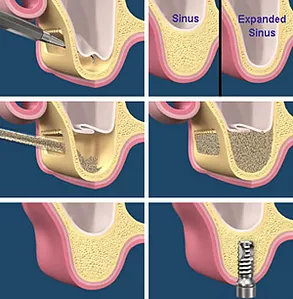
A sinus lift is a surgery that adds bone to the upper jaw, in the area of premolars and molars. It is done when implants are to be placed and there is not enough bone height in the upper jaw or the sinuses are too close to the jaws. Bone loss might be due to-
The loss in volume of bone adversely affects the placement of implants, which rely on the principle of osseointegration. The goal of sinus augmentation is to graft extra bone into the maxillary sinus, so that more bone is available to support implants.
Our oral surgeons first assess the condition by Panoramic radiograph, OPG, or by CT scan, in some cases, to measure sinus’s height and width. The surgery is performed with precision through Ostetome technique or Lateral Window technique, whichever is required.